Physiotherapy: Unleashing the Power of Movement and Laughter
Introduction:
Welcome to the world of physiotherapy, where healing meets humor, and movement becomes medicine. In this comprehensive article, we will embark on a journey through the exciting realm of physiotherapy, exploring its definition, various types of rehabilitation, the importance of movement, the transformative effects it has on the body, and real-life examples that highlight the power of this profession. Get ready to laugh, learn, and discover the wonders of physiotherapy!
Definition of Terms:
Physiotherapy, also known as physical therapy, is a healthcare profession that focuses on optimizing physical function, promoting mobility, and restoring balance in individuals experiencing physical impairments, injuries, or disabilities. It encompasses a holistic approach that combines manual therapy techniques, therapeutic exercises, and patient education to alleviate pain, enhance mobility, and improve overall well-being.
Types of Physiotherapy
There are several types of physiotherapy, each specializing in specific areas of healthcare. Let’s explore some of the most common types of physiotherapy and provide examples to understand them better:
1. Orthopedic Physiotherapy:
Orthopedic physiotherapy focuses on the assessment and treatment of musculoskeletal conditions, such as fractures, sprains, strains, and post-operative rehabilitation. The goal is to restore function, reduce pain, and enhance mobility. Examples of orthopedic physiotherapy interventions include:
- Rehabilitation after joint replacement surgery: Physiotherapists guide patients through exercises and therapies to regain joint mobility, strength, and stability after procedures like hip or knee replacements.
- Sports injury rehabilitation: Athletes recovering from injuries, such as ligament tears or muscle strains, receive specialized physiotherapy treatments to facilitate healing and restore optimal function.
- Back and neck pain management: Physiotherapists employ techniques like manual therapy, exercises, and postural correction to alleviate pain and improve spinal alignment.
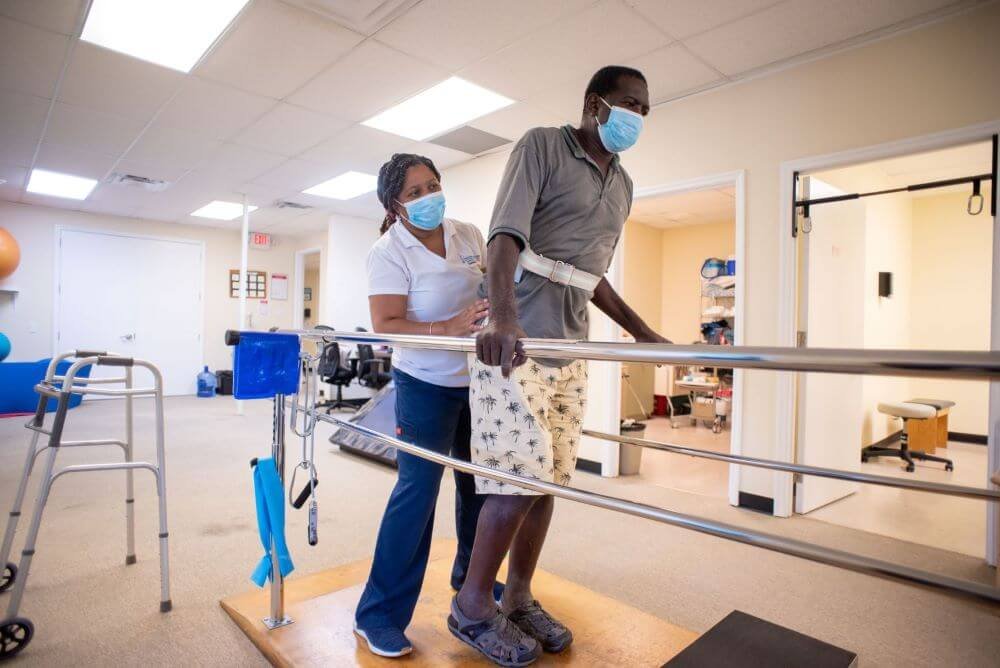

2. Neurological Physiotherapy:
Neurological physiotherapy focuses on treating individuals with neurological conditions that affect the central nervous system, such as stroke, spinal cord injuries, multiple sclerosis, or Parkinson’s disease. The aim is to improve mobility, balance, and overall functional abilities. Examples of neurological physiotherapy interventions include:
- Stroke rehabilitation: Physiotherapists work with stroke survivors to regain motor control, improve balance, and enhance coordination through exercises, gait training, and functional activities.
- Spinal cord injury rehabilitation: Physiotherapy helps individuals with spinal cord injuries improve strength, range of motion, and functional independence using specialized exercises and assistive devices.
- Balance training for Parkinson’s disease: Physiotherapists employ specific exercises and techniques to address balance issues and improve mobility in individuals with Parkinson’s disease.
3. Cardiopulmonary Physiotherapy:
Cardiopulmonary physiotherapy focuses on managing conditions related to the heart and lungs. It aims to enhance cardiovascular fitness, respiratory function, and overall endurance. Examples of cardiopulmonary physiotherapy interventions include:
- Pulmonary rehabilitation for COPD: Physiotherapists design exercise programs and breathing techniques to improve lung function, reduce shortness of breath, and enhance overall endurance in individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Cardiac rehabilitation: Physiotherapy helps individuals recovering from heart surgery or cardiac events improve cardiovascular fitness, manage risk factors, and regain confidence through exercise programs and lifestyle modifications.
4. Pediatric Physiotherapy:
Pediatric physiotherapy specializes in the assessment and treatment of children with developmental delays, congenital disorders, or injuries. The focus is on promoting optimal motor skills, coordination, and overall development. Examples of pediatric physiotherapy interventions include:
- Gross motor skill development: Physiotherapists work with children to enhance their motor skills, such as crawling, walking, running, and jumping, through play-based therapy, exercises, and activities.
- Cerebral palsy management: Physiotherapy interventions help children with cerebral palsy improve muscle tone, coordination, and mobility, facilitating their participation in daily activities and maximizing their functional abilities.
These are just a few examples of the types of physiotherapy available. Other specialized areas include geriatric physiotherapy, women’s health physiotherapy, and sports physiotherapy, among others. Each type of physiotherapy addresses specific conditions and goals, tailored to the unique needs of individuals to promote healing, enhance function, and improve overall well-being.

The Importance of Movement in Physiotherapy:
Movement lies at the heart of physiotherapy, and here’s why it’s so crucial:

- Pain Relief: Engaging in appropriate movement and therapeutic exercises helps release endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers, reducing discomfort and promoting pain relief.
- Restoring Function: Physiotherapy aims to restore individuals’ ability to perform daily activities, regain independence, and participate in hobbies or sports they love. It focuses on improving mobility, strength, and flexibility to enhance functional capacity.
- Injury Prevention: Through targeted exercises, movement analysis, and education, physiotherapy helps identify and address risk factors, improving biomechanics, and reducing the likelihood of future injuries.
- Enhancing Performance: Athletes and individuals seeking to optimize their physical performance can benefit from physiotherapy interventions that improve strength, flexibility, and movement efficiency.
The Transformative Effects of Physiotherapy:

Physiotherapy has remarkable effects on the body, fostering healing and empowering individuals to lead healthier lives. Consider the following:
- Improved Mobility and Flexibility: Physiotherapy techniques, such as joint mobilization, stretching, and therapeutic exercises, enhance joint range of motion, flexibility, and overall mobility.
- Enhanced Strength and Stability: Through targeted exercises and resistance training, physiotherapy strengthens muscles, improves stability, and enhances functional abilities.
- Efficient Movement Patterns: Physiotherapy helps individuals develop proper movement patterns, correcting postural imbalances and promoting efficient biomechanics for daily activities and sports performance.
- Faster Recovery and Rehabilitation: Physiotherapy interventions expedite recovery after surgeries or injuries, facilitating tissue healing, reducing inflammation, and optimizing rehabilitation outcomes
- Pain Management and Reduction: Physiotherapy techniques, such as manual therapy, electrotherapy, and therapeutic exercises, effectively alleviate pain and discomfort associated with various musculoskeletal and neurological conditions.
- Improved Balance and Coordination: Physiotherapy interventions focus on enhancing balance, coordination, and proprioception, reducing the risk of falls and improving overall movement control.
- Respiratory Enhancement: Cardiopulmonary physiotherapy helps individuals with respiratory conditions improve lung capacity, breathing patterns, and clearance of secretions, leading to better overall respiratory function.
- Rehabilitation for Neurological Conditions: Physiotherapy plays a vital role in helping individuals with neurological conditions regain motor function, improve balance, and enhance independence in daily activities.
Humor, Practical Cases, and Interactive Questions:
Let’s infuse some humor into our journey through physiotherapy! Picture this: a patient attempting to balance on a wobbly exercise ball, only to end up bouncing and rolling across the room. Laughter is indeed a therapeutic tool that can lighten the mood during physiotherapy sessions, making the process enjoyable and engaging.
Now, let’s dive into some practical cases and examples. Meet Sarah, a determined individual who suffered a sports injury and underwent surgery. With the help of her physiotherapist, she embarked on a rehabilitation program involving a combination of manual therapy, strengthening exercises, and functional training. Over time, Sarah regained her strength, improved her range of motion, and eventually returned to her beloved sport with even better performance.
Interactive Questions and Answers:
- Q: Can physiotherapy help with chronic pain conditions? A: Absolutely! Physiotherapy offers various modalities, exercises, and techniques to manage chronic pain, improve function, and enhance overall quality of life.
- Q: How long does a typical physiotherapy session last? A: Session durations can vary depending on the individual’s needs and treatment plan. On average, a session may last 30 to 60 minutes.
- Q: Can physiotherapy be beneficial for children with developmental delays? A: Yes! Pediatric physiotherapy focuses on promoting motor skills, coordination, and overall development in children with various conditions or delays.
Conclusion
Physiotherapy is a remarkable discipline that empowers individuals to overcome physical challenges, regain function, and live healthier, more fulfilling lives. By harnessing the power of movement, laughter, and personalized care, physiotherapists bring healing and transformation to patients of all ages and backgrounds. Whether it’s recovering from an injury, managing chronic pain, or enhancing athletic performance, physiotherapy offers a comprehensive approach that focuses on restoring mobility, improving strength, and optimizing overall well-being. So, embrace the journey of physiotherapy, and let the power of movement set you on a path to a healthier and happier you!